Transmedia Storytelling Project
Executive Summary of The Holler Video Storytelling Project
Participants:
9 Teachers and 150 Students across 22 counties in Eastern Kentucky (Grades 3-12).
Digital storytelling, specifically video production, requires knowledge of many subjects and topics within those content areas, but foundational material can be taught using a specific set of skills. Thinking visually, interviewing and connecting with people, planning production, using video cameras, framing shots and capturing action, and finally editing footage to form a finished product. By mastering these fundamental skills, students can concentrate their efforts on content and focus on creating professional products. Young producers can often be frozen by the technical skills needed or preconceived notions that one must possess the right equipment before beginning a project, and they cannot progress beyond these challenges. Completion of this supplemental material will allow for more classroom time to focus on content and for hands-on use of the equipment, and the general crafting of ideas.
Terminal Objective:
Upon completion of the Transmedia video production course, students will understand the ideas and practices needed to develop an idea for digital video production, plan the production, shoot the material needed for the production, and edit the material into a final product that will be distributed on The Holler. Students will be able to identify key concepts in storytelling methods and the threads of a potential story to build visual sequences and scenes for their video. Students should be able to identify qualities in digital stories they like or find interesting and apply those same threads and thoughts to their own work.
Enabling Objectives:
- Students will be able to identify viable subjects for short digital videos.
- What story do you want to tell? What is interesting about this specific story?
- What are the visual sequences needed to tell this story?
- Why is this interesting and who will the potential audience be? Is it universal or niche?
- Students will be able to create shot lists, interview questions, and camera schematics for video productions.
- Students can identify the shots needed before going on a shoot and are visualizing the scenes in their minds. This can be shown through storyboard and proper shot lists and interview questions.
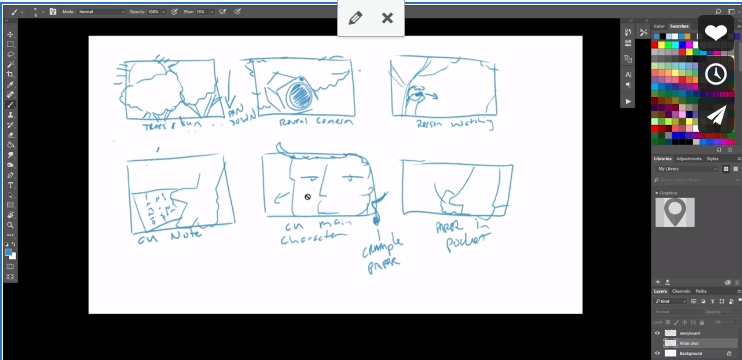
- Students will be able to create storyboards showing scenes of the films they want to make.
- Storyboards do not need to be complex drawings; stick figures and motion arrows work best. The purpose of the storyboard is to establish screen space and flow before going on a shoot. Some things will obviously change as the shoot unfolds, but going in with a plan will help the students stay focused and attentive. The key to a good shoot is not feeling lost or just filling time, students must execute a plan, be focused, and be aware of people’s time commitments and schedules.
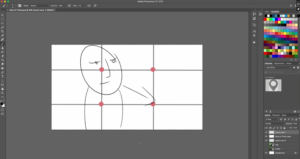
- Students will be able to identify and use Master Scene shot selection, the 180 Degree Rule, and the Rule of Thirds.
- Students will know how to incorporate wide, medium, and close-up shots for optimum visual storytelling methods.
- Students will know how to keep up the willful suspension of disbelief needed for successful filmmaking and understand how the 180-degree rule plays into that success.
- Students will be able to identify the following terminology:
- White balance
- Gain
- Iris/F-stop
- Depth of Field
- Students will be able to organize footage in a non-linear editing system.
- Students will know how to create bins
- Students will know how to create sequences
- Students will know how to create sub-clips
- Students will be able to create a rough and final cut of a short documentary film.
- Students will assemble an edit by marking in/out points through clips and dropping them on the timeline
- Students will understand the difference between a rough cut, fine cut, and final edit
- Students will learn to assemble non-linear footage to tell a greater story
Student Assessment:
- Students will complete a short series of terminology quizzes.
- Students will turn in written production plans that will be assessed by a provided rubric.
- Students will complete a peer review of all plans produced in the class and will be assessed based on their ability to discuss the work using the proper terminology.
- Students will write a paper that describes the major units learned in this course as they’re applied and analyzed by a short digital video of their choice.
Teacher Assessment:
- Teachers will evaluate their own challenges and procedures through a 500-700 word Holler post.
- Teachers will grade assignments and assess student needs after each major module
- Teachers will collaborate using a shared document to plan for future Trans Media initiatives and create a rubric for generating online course content
- Teachers will present at both KVEC FIREsummit conferences, discussing their ideas, execution, and program results..
Project Completion and Evidence:
Teacher participant blogs (written at the beginning of the project):
Teacher Sample Post 1:
https://www.theholler.org/holler-out-loud/
Teacher Sample Post 2:
https://www.theholler.org/create-and-be-heard/
Teacher Video Presentations (produced at the end of the project)
Teacher Video 1:
https://summit.theholler.org/speaker/rebecca-potter-2/
Teacher Video 2:
https://summit.theholler.org/speaker/brian-hobbs/
Student Work:
- 3rd Grade Sample
- High School Samples